Business Structures
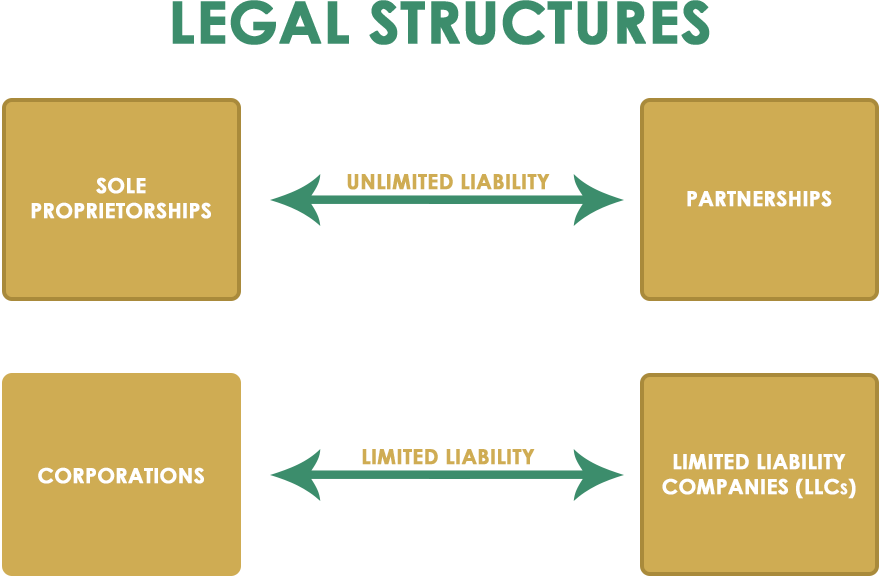
Sole proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the simplest business to form, it gives you complete control of your business. You’re automatically considered to be a sole proprietorship if you do business activities but don’t register as any other kind of business.
Sole proprietorships do not produce a separate business entity. This means your business assets and liabilities are not separate from your personal assets and liabilities. You may be held personally liable for the debts and obligations of the business. Sole proprietors can file for a DBA trade name to operate as their official business name.
Partnership
Partnerships are the simplest structure for two or more persons to own a business together. There are two common kinds of partnerships: limited partnerships (LP) and limited liability partnerships (LLP).
A partnership is a form of business where two or more people share ownership, as well as the responsibility for managing the company and the income or losses the business generates.
Limited liability company (LLC)
A limited liability company (LLC) is a business structure in which the owners are not personally liable for the company’s debts or liabilities. An advantage of a Limited liability company is you reap the benefits of and mirror the characteristics of corporation and partnership business structures.
Corporation (C corp)
A corporation, commonly known as a C corp, is a legal entity that’s separate from its owners. C corporations, the most powerful of corporations, are also subject to corporate income taxation. The taxing of profits from the business is at both corporate and personal levels, creating a double taxation situation. Basically, starting a C Corp has much more stringent requirements than other entities.